Working Memory: Updating - Spatial (DATEUP) Module
Model 65325
The DATEUP training program trains the executive updating function of spatial working memory. Updating is the ability to renew memory contents in a controlled and goal-directed manner.
Setting and Task
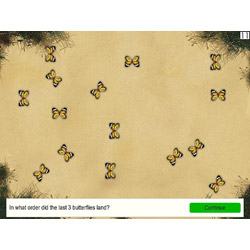
The client watches butterflies in a natural setting as they fly over flower meadows and sandy ground. From time to time one butterfly lands and another starts its flight etc. until eventually, at irregular intervals, the client is asked a question. Depending on the type of task, the client must now highlight one or more butterflies - for example the last but one butterfly, the last three butterflies or the last of each of three different butterfly types.
Theory
Updating information is a fundamental cognitive process. New stimuli and information from perception or long-term memory bombard us constantly and replace older versions – continuous updating is required. For example, driving in a city involves a rapid and continuous process in which observed situations are briefly stored, compared with newly perceived ones and immediately replaced - for instance if a number of vehicles are approaching an unsigned junction and it is necessary to decide who has priority. At the same time, information from long-term memory is activated in order to identify what has been perceived and process it in a goal-directed manner; for example, on European roads this will involve recalling the rule which states that drivers must give way to traffic from the right. In the scientific literature updating is regarded as one of the basal executive control mechanisms of working memory. These mechanisms are used to control and coordinate cognitive processes and form the basis for more complex cognitive processing. The executive functions of working memory can be improved through repetitive training (Olesen et al., 2004; Erickson et al., 2007; Jaeggi et al., 2008; Dahlin et al., 2008). The DATEUP program trains the updating function by means of tasks of three types that are widely used and well-confirmed in the literature: running tasks, keep-track tasks and n-back tasks. The aim of training is to achieve more flexible and more automated updating of material in spatial working memory and to improve complex cognitive functions.
Difficulty Structure
The DATEUP training program has 25 difficulty levels. The demands on working memory are heightened mainly by increasing the number of stimuli (butterflies) that the client must retain and update. The three types of task (n-back, running, keep-track) occur one after the other across the different levels; at the highest levels they are combined to form new task variants. As the level increases both the number of butterflies on the screen and their speed also increase. In addition, the timing of the questions becomes increasingly unpredictable as the client progresses through the levels.
